United States Frost Depths for Residential Structures
Last Update: December 6, 2024
Frost Depth Interactive Map
The custom map below depicts the United States residential building code frost depth by jurisdiction based on our research. The information presented in this map is the most comprehensive database of building code frost depths on the internet, covering about 60% of the US residential population. You can use this like normal Google Maps by zooming and panning to your location, or by searching by city, county, state, or ZIP code. This map will be periodically updated as we find further information, so check back later if your location is not given!
What is Frost Depth?
Frost depth (or the “frost line”) is the depth in the soil above which water may freeze during the winter. Colder areas with longer winters have deeper frost depths, and areas with milder winters have shallow or no frost depth. Water expands when it freezes. Placing a foundation above the frost depth could allow water to freeze below the foundation and lift it, which is called “frost heave.” This can lead to all sorts of issues, from cracked foundations to leaning structures.
How Does Frost Depth Impact My Pergola Installation?
An important step in the construction of your pergola is to place the pier foundations below the local frost depth. Doing so will avoid issues with frost heave, keeping your pergola stable and level throughout its life.
How Do I Find My Local Frost Depth?
Finding your local frost depth can be challenging if you don’t know where to start. To assist you, we’ve done the research already and have summarized it by State in the sections below and interactive map above. Sources of information are given so you can independently verify.
If information for your local frost depth is not available below, you can find this yourself. There are several places you can check to do so:
Contact your city or county Building Department. They should be able to tell you very easily.
Perform an online search. We recommend the following search terms (in order of likelihood of helpful result):
- [city name] municipal code, then search for the term “frost”
- [city name] frost depth
- [city name] building code
- [city name] residential code
- [city name] design criteria
- [city name] minimum footing depth
- [city name] Table R301.2
If these search terms do not immediately yield an answer, you may have to search through different documents on the city/county website to find what you’re looking for. We’ve found that this information can sometimes be found in a city’s Deck Guidelines document.
Minimum Foundation Depth
Regardless of the defined frost depth for your area, you should install your pergola piers no shallower than 12″, unless you have bedrock that projects shallower than that. This is the minimum foundation depth permitted by the IBC (Section 1809.4) and the IRC (Section R403.1.4). Most municipalities have either adopted the IBC/IRC or use it as a model code.
Nomenclature
IBC = International Building Code
IRC = International Residential Code
Disclaimer
Note that the information below is provided for reference purposes only, may be out of date, and only applies to residential construction. You should always check with your local Authority Having Jurisdiction (likely the local Building Inspector) to confirm that you are using the correct frost depth. If you find that any of our information is in error, please let us know.
Frost Depth by State
Alabama
The minimum frost depth for Alabama is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Alabama are given below:
Birmingham: 12″ (Jefferson County Building Code, amended July 9, 2020, Section 114)
Montgomery: 12″ (Ordinance #15-2020, Section V.A.5)
Mobile: 12″ (as defined by amendment to the 2021 International Residential Code, Table R301.2).
Alaska
The minimum frost depth for Alaska is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Additionally, a large part of Alaska is covered in permafrost, which has its own unique design requirements. Contact your local Building Department for further information on foundation depths. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Alaska are given below:
Anchorage: 120″ for cast-in-place concrete piers, which may be reduced to 60″ in non-frost-susceptible soils (2018 Local Amendments, Chapter 23.85, Table R403.1)
Fairbanks: 42″ (Ordinance 6153, amendment to IRC Table R301.2(1))
Juneau: 32″ (City and Borough of Juneau Code, Section 19.04)
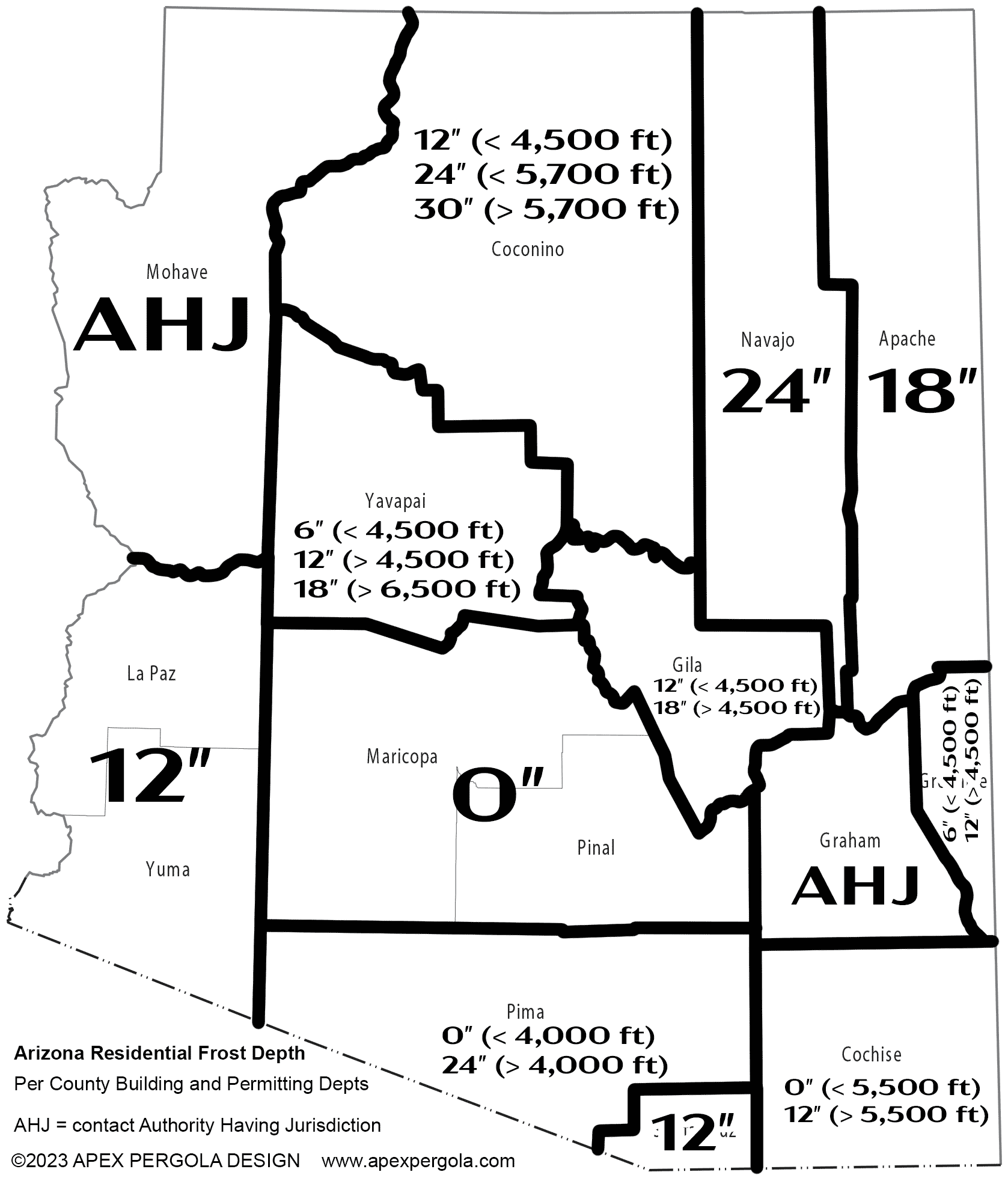
Arizona
The minimum frost depth for Arizona is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. See the image at right for the residential frost depth by county in Arizona. Note that foundations should be installed a minimum of 12″ deep, regardless of the minimum frost depth.
Arkansas
The minimum frost depth for Arkansas is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Arkansas are given below:
Little Rock: 12″ (City of Little Rock Codes & Design Criteria, effective January 1, 2014)
Fort Smith: 12″ (2021 Arkansas State Fire Prevention Code Volume III, Section R403.1.4)
Fayetteville: 12″ (2021 Arkansas State Fire Prevention Code Volume III, Section R403.1.4)
California
The minimum frost depth for California is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in California are given below.
Los Angeles: 12″ (2020 City of Los Angeles Residential Code, Table R301.2(1))
San Diego: no defined frost depth (City of San Diego 2013 Residential Building Regulations, Table 149.0302)
San José: 5″ (Municipal Code of San José, Title 24, Section 24.09.225)
Colorado
The minimum frost depth for Colorado is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Colorado are given below.
Denver: 36″ (2022 Denver Building Code & Denver Fire Code, Section 1809.5)
Colorado Springs: 30″ (Pikes Peak Regional Building Code, 2023 Edition, Section RBC302.4.63)
Aurora: 36″ (Aurora City Code, Article V, Chapter 22, Section 22-186)
Connecticut
The minimum frost depth for Connecticut is 42″ (2022 Connecticut State Building Code, Amendments to 2021 IRC, Table R301.2(1)).
Delaware
The minimum frost depth for Delaware is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction (see image at right). Frost depths for the three counties in Delaware are given below.
New Castle County: 32″ (Code of Ordinances, Chapter 6, Article 5, Section 6.05.002, Table R301.2(1))
Kent County: 24″ (County Code, Part 2, Article IV, Section 105-24, Table R301.2(1))
Sussex County: 24″ (Sussex County building code website)
Florida
Florida has no defined frost depth (2020 Florida Building Code, Residential, 7th Edition, Table R301.2(1)). Pergola pier foundations should be installed to a minimum depth of 12″, or as indicated on your drawings.
Georgia
There is no minimum frost depth defined statewide for Georgia. The minimum required foundation depth is 12″ (2018 IRC with Georgia Amendments, Section R403.1.4). Note that some jurisdictions may require a deeper foundation depth or define a frost depth deeper than 12″, though we did not find any in our research.
Hawaii
The minimum frost depth for Hawaii is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. For most non-mountain locations, there will be no defined frost depth. In this instance, pergola pier foundations should be installed to a minimum depth of 12″ (2018 IRC with Hawaii Amendments, Section R403.1.4), or as indicated on your drawings.
Idaho
The minimum frost depth for Idaho is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Idaho are given below.
Boise: 24″ (City of Boise, Current Building Codes webpage)
Meridian: 24″ (Meridian, ID Design Criteria)
Nampa: 24″ (Code of Ordinances City of Nampa, Idaho, Title 4, Chapter 2, Section 4-2-2, Table R301.2(1))
Illinois
The minimum frost depth for Illinois is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Illinois are given below.
Chicago: 42″ (2019 Chicago Building Code, Section 1809.5)
Aurora: 42″ (City of Aurora Code of Ordinances, Chapter 12, Division 12-II-7, Section 12.17-6, Table R301.2(1))
Rockford: 42″ (local amendments to IRC, Table R301.2(1))
Indiana
The minimum frost depth for Indiana is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Table R301.2(1) of the 2020 Indiana Residential Code defines the minimum frost depth by county. The range is from 24″ to 36″ (see the image at the right), so one could install foundations to 36″ and satisfy the requirements of any county in the state.
Iowa
The minimum frost depth for Iowa is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Iowa are given below.
Des Moines: 42″ (City of Des Moines, Adopted Construction Codes webpage)
Cedar Rapids: 42″ (Cedar Rapids Municipal Code, Chapter 33, Section 33.23, Table R301.2(1))
Davenport: 42″ (City of Davenport Municipal Code, Section 15.12.052, Table R301.2(1))
Kansas
The minimum frost depth for Kansas is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Kansas are given below.
Wichita: 24″ (2018 IRC with Amendments, Table R301.2(1))
Overland Park: 36″ (Overland Park Municipal Code, Title 16, Section 16.110.R301.2(1))
Kansas City: 36″ (Unified Government Code of Wyandotte County/Kansas City, Chapter 8, Article VII, Section 8-412, Table R301.2(1))
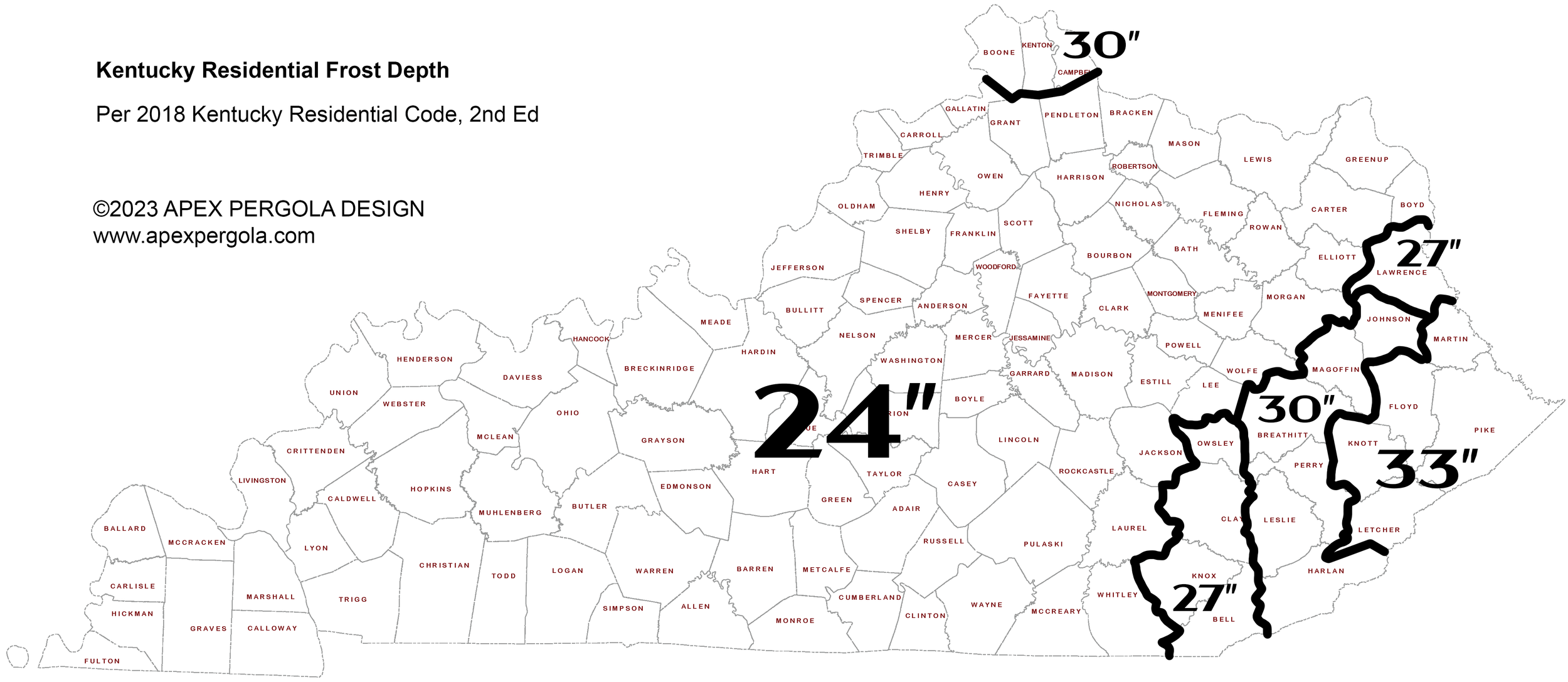
Kentucky
The minimum frost depth for Kentucky is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Table R403.1.4 of the 2018 Kentucky Residential Code, 2nd Edition defines the minimum frost depth by county (see image below). The range is from 24″ to 33″, so one could install foundations to 33″ and satisfy the requirements of any county in the state.
Louisiana
Foundation requirements for Louisiana vary by jurisdiction. Minimum foundation depths for the three most populous cities in Louisiana are given below.
New Orleans: no defined frost depth; however, the City amendments to the IBC (Code of Ordinances City of New Orleans, Louisiana, Chapter 26, Article I, Section 26-14, Subsection 1811.3.1) requires that foundations be supported on piles unless a Geotechnical analysis provides otherwise. We recommend you contact the Building Department for further information and guidance.
Baton Rouge: 12″ (2021 IRC with Louisiana Amendments, Section R403.1.4)
Shreveport: 12″ (2021 IRC with Louisiana Amendments, Section R403.1.4)
Maine
The minimum frost depth for Maine is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Maine are given below.
Portland: 48″ (given in the city’s Deck Guidelines)
Lewiston: 48″ (given in the city’s Uncovered Decks and Porches Building Guide)
Bangor: 60″ (City of Bangor Building Codes webpage)
Maryland
The minimum frost depth for Maryland is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. See the image below for the Maryland and Washington D.C. residential frost depth map.
Massachusetts
The minimum frost depth for Massachusetts is 48″ (Ninth Edition of the MA State Building Code 780, Residential Code, Chapter 3, Table R301.2(1)).
Michigan
The minimum frost depth for Michigan is 42″ (2015 Michigan Residential Code, Table R301.2(1)). Local conditions may require deeper frost depths (Section R403.1.4).
Minnesota
The frost depth for Minnesota depends on Zone (Minnesota Administrative Rules 1303.1600). See the map of Minnesota at the right with the demarcation between Zones and the appropriate frost depth. Generally, north of St. Cloud has a 60″ frost depth, and south has 42″.
Mississippi
The minimum frost depth for Mississippi is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Minimum foundation depths for the three most populous cities in Mississippi are given below.
Jackson: 12″ (2018 IRC with Mississippi Amendments, Section R403.1.4)
Gulfport: 12″ (2018 IRC with Mississippi Amendments, Section R403.1.4)
Southaven: 12″ (2018 IRC with Mississippi Amendments, Section R403.1.4)
Missouri
The minimum frost depth for Missouri is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Missouri are given below.
Kansas City: 36″ (Code of Ordinances of Kansas City, Missouri, Chapter 18, Article III, Section 18-57, Table R301.2(1))
St. Louis: 30″ (Code of the City of St. Louis, Title 25, Chapter 25.11, Section 25.11.010, Table R301.2(1))
Springfield: 24″ (Land Development Code City of Springfield, Missouri, Article XIII, Section 36-1302, Table R301.2(1))
Montana
The minimum frost depth for Montana is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Montana are given below.
Billings: 42″ (Billings Building Design Criteria)
Missoula: unknown
Great Falls: 42″ (City of Great Falls, Building & Construction Guide website)
Otherwise, for areas of the state outside of certified local government jurisdictions, the minimum depth from finished grade to the bottom of footings is 36″ for single story wood or metal frame buildings or 48″ for multistory or masonry buildings (Administrative Rules of the State of Montana, Section 24.301.142).
Nebraska
The minimum frost depth for Nebraska is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Nebraska are given below.
Omaha: 42″ (Municipal Code City of Omaha, Nebraska, Chapter 43, Article II, Division 2, Section 43-127, Table R301.2(1))
Lincoln: 36″ (local amendment to IRC)
Bellevue: 42″ (Bellevue, Nebraska Code of Ordinances, Chapter 8, Section 8-18.6, Table R301.2)
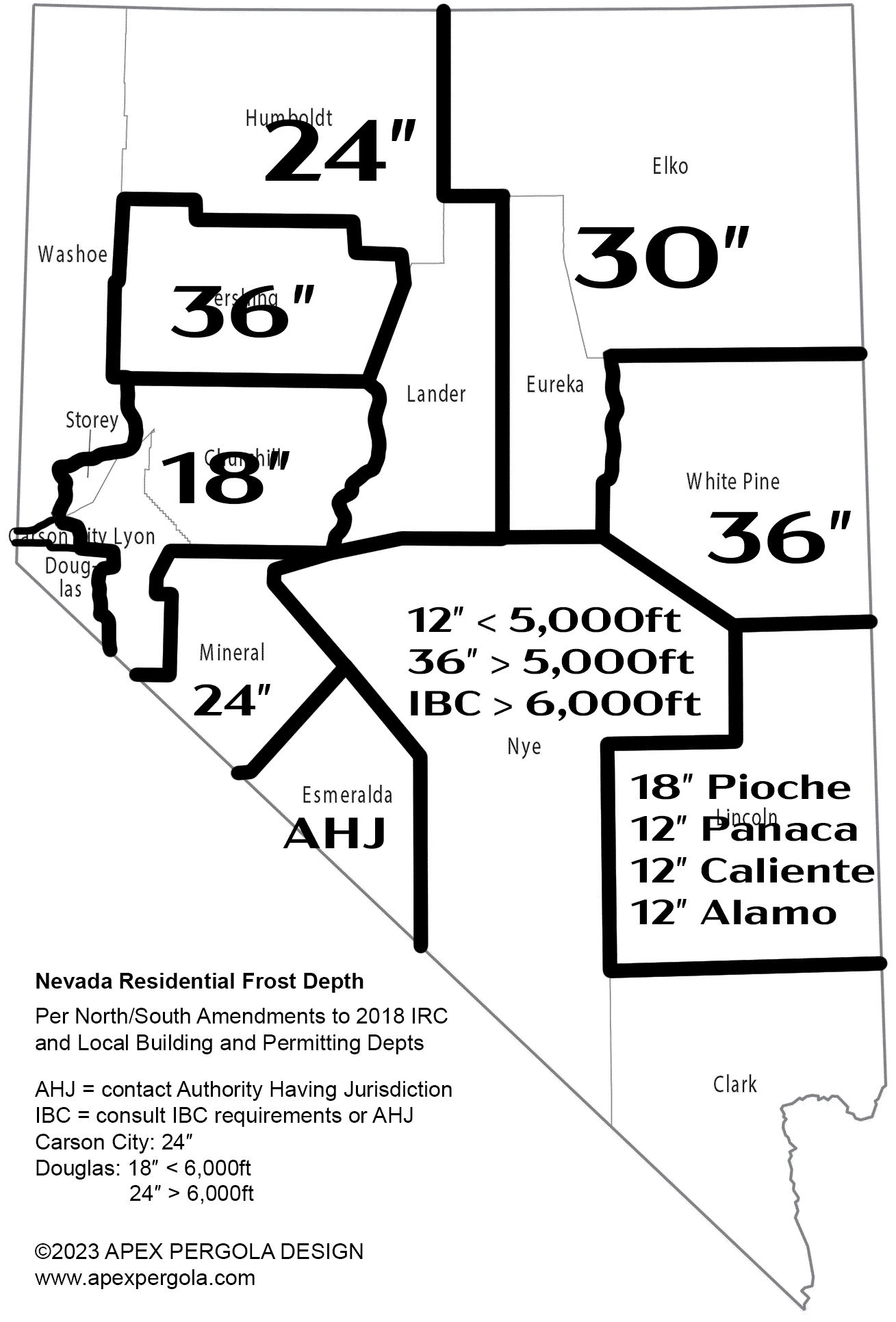
Nevada
The minimum frost depth for Nevada is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Some locales define the minimum frost depth on a countywide basis, and others have specific frost depths per jurisdiction. See the image at right for the Nevada residential frost depth map.
New Hampshire
The minimum frost depth for New Hampshire is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Nevada are given below.
Manchester: 48″ (amendment to the 2018 IRC)
Nashua: 48″ (City of Nashua Code, Article II, Section 105-11.D)
Concord: 48″ (Code of Ordinances City of Concord, NH, Title III, Chapter 26, Section 26-1-10)
New Jersey
The minimum frost depth for New Jersey is 30″ for southern parts and 36″ for northern parts (UCC One- & Two-Family Dwelling Subcode, Table R301.2). South New Jersey consists of Monmouth and Burlington Counties and all counties south. North New Jersey consists of Mercer and Middlesex Counties and all counties north. See the map at right for the line of demarcation.
New Mexico
The minimum frost depth for New Mexico is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in New Mexico are given below.
Albuquerque: 16″ (City’s informational handout on New Residential Construction)
Las Cruces: 6″ (Development Code Part III City of Las Cruces, New Mexico, Chapter 30, Article II, Division 17, Section 30-722, Table R301.2(1))
Rio Rancho: 18″ (City of Rio Rancho, Building Division webpage)
New York
The minimum frost depth for New York is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in New York are given below.
New York City: 48″ (2022 Construction Codes, Building Code, Section 1809.3.1)
Buffalo: 48″ (City of Buffalo website)
Rochester: 48″ (Rochester City Code, Part II, Article III, Section 39-309.B)
North Carolina
The minimum frost depth in North Carolina is 12″ (2018 North Carolina State Building Code: Residential Code, Table R301.2(1)). Local frost depths in excess of 12″ may be applicable.
North Dakota
The minimum frost depth for North Dakota is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in North Dakota are given below.
Fargo: 54″ (local amendment to IRC, Table R301.2)
Bismarck: 48″ (City of Bismarck, Building and Design Criteria webpage)
Grand Forks: 60″ (local amendment to 2021 IBC, Section 1809.7(C)4)
Ohio
The minimum frost depth for Ohio is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Ohio are given below.
Columbus: 32″ (Columbus City Codes, Title 41, Chapter 4125, Section 4125.03)
Cleveland: 36″ for one- and two-family residential structures (Cleveland, OH Code of Ordinances, Part IIIE, Title XIII, Section 3125.06)
Cincinnati: 30″ (minimum depth of footings for decks per the City’s Deck Plan)
Oklahoma
The minimum frost depth for Oklahoma is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Oklahoma are given below.
Oklahoma City: 18″ (local amendment to IRC, Table R301.2(1))
Tulsa: 18″ (Tulsa Code of Ordinances, Title 51, Chapter 2, Section 201, Chapter 3)
Norman: 18″ (City of Norman Municipal Code, Chapter 6, Article 6-II, Section 6-209(d)(20))
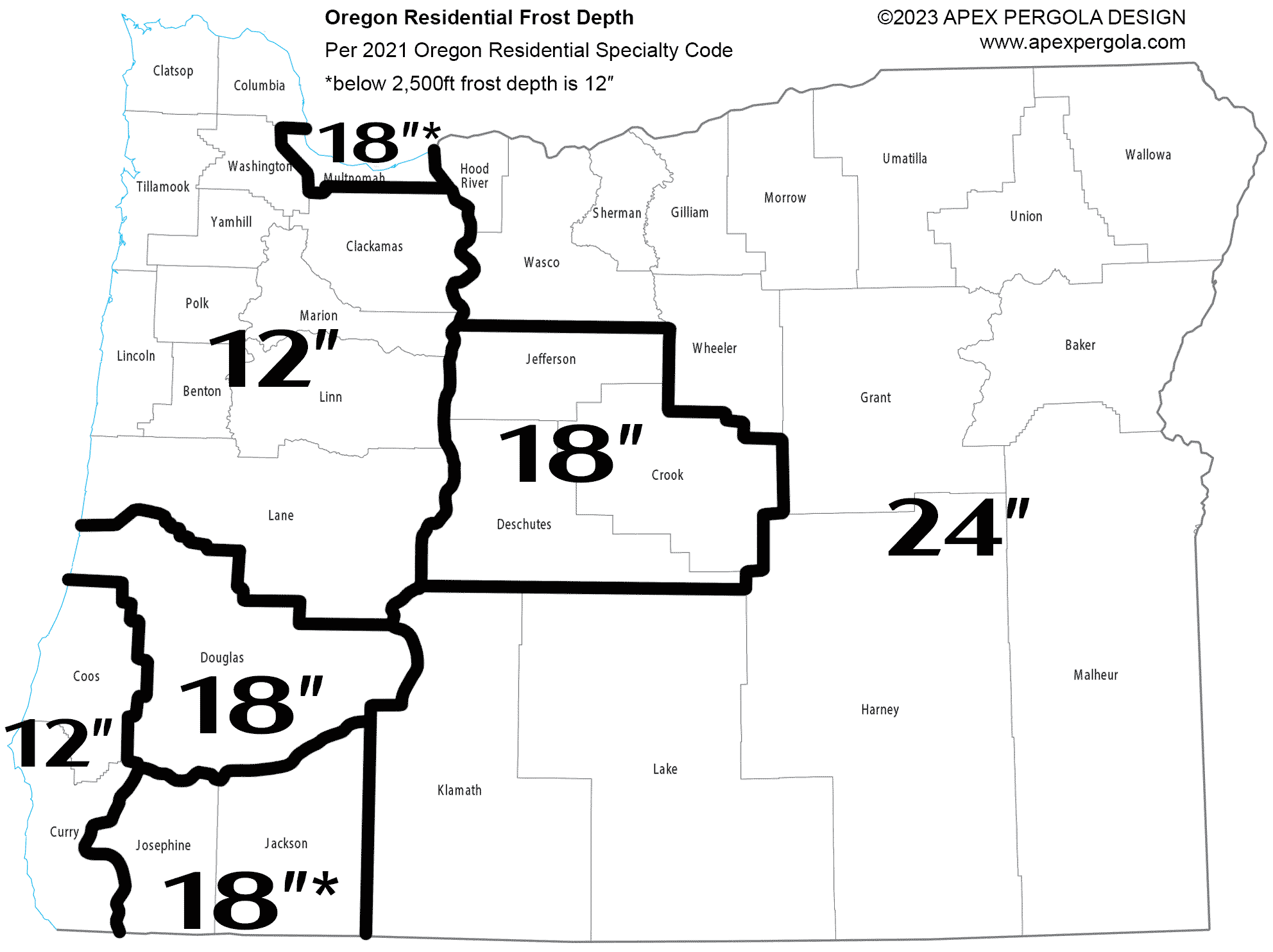
Oregon
The minimum frost depth for Oregon is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Table R301.2(1) of the 2021 Oregon Residential Specialty Code defines the minimum frost depth by county (see image below). The range is from 12″ to 24″, so one could install foundations to 24″ and satisfy the requirements of any county in the state.
Pennsylvania
The minimum frost depth for Pennsylvania is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Pennsylvania are given below.
Philadelphia: 30″ (The Philadelphia Code, Title 4, Subcode “R,” Part III, Chapter 3, Table R301.2)
Pittsburgh: 36″ (Code of Ordinances City of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Pittsburgh Zoning Code, Title Ten, Section 1002.02, Table R301.2)
Allentown: 36″ (City of Allentown Code, Part II, Chapter 225, Section 225-2, amendment to IBC Section 1805.4.1.3)
Rhode Island
The minimum frost depth in Rhode Island is 40″ (RISBC-2 Rhode Island State One and Two Family Dwellings, Table R301.2(1)), except for New Shoreham, which is 30″.
South Carolina
The minimum frost depth for South Carolina is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Minimum foundation depths for the two most populous areas in South Carolina are given below.
Columbia: 12″ (2021 South Carolina Residential Code, Section R403.1.4)
Charleston & metro area: 12″ (2021 South Carolina Residential Code, Section R403.1.4)
South Dakota
The minimum frost depth for South Dakota is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in South Dakota are given below.
Sioux Falls: 42″ (local amendment to IRC, Table R301.2)
Rapid City: 42″ (Rapid City, SD Code of Ordinances, Title 15, Section 15.13.070)
Aberdeen: 48″ (Aberdeen City Code, Chapter 12, Article II, Division 2, Section 12-21, Table R301.2(1))
Tennessee
The minimum frost depth for Tennessee is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Tennessee are given below.
Nashville: 12″ (local amendment to IBC/IRC, Table R301.2(1))
Memphis: 5″ (local amendment to IRC, Table R301.2(1))
Knoxville: 12″ (Code of Ordinances City of Knoxville, Tennessee, Chapter 6, Article IIA, Section 6-42, Table R301.2(1))
Texas
The minimum frost depth for Texas is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Texas are given below.
Houston: 6″ (local amendment to IRC, Table R301.2(1))
San Antonio: 0″ (local amendment to 2021 IRC, Table R301.2)
Dallas: 6″ (local amendment to IRC, Table R301.2)
Additionally, the Texas Administrative Code 10.1.80.B, Rule §80.21(i)(1) provides a 12″ frost line depth for the installation of manufactured (mobile) homes in a number of counties.
Utah
The minimum frost depth for Utah is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Some locales define the minimum frost depth on a countywide basis, and others have specific frost depths per jurisdiction. See the image at right for the Utah residential frost depth map.
Vermont
The minimum foundation depth in Vermont is 60″ (Vermont Fire and Building Safety Code, 2015 edition, Section 1809.5). Local frost depths in excess of 60″ may be applicable.
Virginia
The minimum frost depth for Virginia is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Virginia are given below.
Virginia Beach: 12″ (local amendment to IRC Table R301.2(1))
Norfolk: 12″ (Code of the City of Norfolk, Virginia, Chapter 11.1, Section 11.1-4.2)
Chesapeake: 12″ (Chesapeake Residential R-5 Construction Information List)
Washington
The minimum frost depth for Washington is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in Virginia are given below.
Seattle: 12″ (Seattle Residential Code, Table R301.2(1))
Spokane: 12″ (Spokane Code of Ordinances, Title 3, Section 3.02.040)
Tacoma: 12″ (Tacoma Municipal Code, Title 2, Table R301.2(1))
Washington D.C.
The minimum frost depth for Washington D.C. is 30″ (D.C. Municipal Regulations, Section 12-A1809).
West Virginia
The minimum frost depth for West Virginia is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Frost depths for the three most populous cities in West Virginia are given below.
Charleston: 24″ (Charleston Building Department Administrative Manual)
Huntington: unknown, probably 24″
Morgantown: 30″ (Code of Ordinances City of Morgantown, West Virginia, Part 17, Article 1713, Section 1713.01(h)(8))
Wisconsin
The minimum frost depth in Wisconsin is 48″ (One- & Two-Family Uniform Dwelling Code, Section SPS 321.16). Local frost depths in excess of 48″ may be applicable.
Wyoming
The minimum frost depth for Wyoming is not defined statewide and varies by jurisdiction. Some locales define the minimum frost depth on a countywide basis, some do not enforce a building code, and others have specific frost depths per jurisdiction. See the image below for the Wyoming residential frost depth map. For locations where no building code is enforced, we recommend a minimum of 42″ be used, or consult a local building professional.
Instructions provided by Apex Pergola Design are solely for informational purposes and are provided without warranties or guarantees of any kind. Builder/Installer is solely responsible for construction of the pergola and shall be responsible for identifying, reviewing, and complying with the applicable building codes in effect at the time of pergola construction and ensuring the pergola construction complies with such building codes and requirements. Apex Pergola shall not be liable for any claim, loss or damage arising out of: (a) any misuse or unauthorized usage of the Plans provided; (b) any constructions, structures or designs made by the Client or a third party on the basis and in reliance on the Plans or (c) any other circumstances beyond Apex Pergola’s reasonable control.